
Next: About this document ...
WHAT IS COSMOLOGY?
Cosmology answers, or pretends to answer, questions like that:
- Was there a beginning of the universe?
- What is the nature of the universe?
- What role do humans play in the universe?
In ancient cosmologies questions about the Earth and the Sun were also
part of cosmology:
- What makes the Sun rise, and what carries it across the sky?
- Where does the Sun go at night?
- What is the shape of the Earth?
The modern cosmology also seeks answers to the following questions:
- Is the universe open, flat, or closed?
- What is the age of the universe?
- What is the nature of the dark matter?
The future cosmology will study questions like that:
- Why is tachionoretic intraserrence present in chuomatic
quasisurtics?
- What do fartinating untenarts decay into?
As we try to understand the universe around us, the scope of our
understanding, and the questions we ask, are necessary limited by the
finite amount of our knowledge. We can only pose questions, answers to
which we can understand. And whatever lies beyond our understanding,
is beyond our knowledge either...
MYTHOLOGY VERSUS SCIENCE
Cosmology started not as science, but as mythology, i.e. a
set of beliefs about the structure of the (ancient) world.
The main part of almost all ancient myths is anthropocentrism,
the belief that humans occupy a special place in the universe.
 Why does the universe seem to be made for
humans? Look, we get everything we need for our life from the nature around
us: water, food, fuel, materials for construction, etc.
Why does the universe seem to be made for
humans? Look, we get everything we need for our life from the nature around
us: water, food, fuel, materials for construction, etc.
- A:
- Clearly the universe and the Earth are designed for humans.
- B:
- O man, this is just a coincidence.
- C:
- Humans are adapted to life on the Earth, i.e. we require
for life only what the Earth can provide.
- D:
- This is not true at all! My car is not made by nature, it is
made by people!
The story of modern cosmology is the story of unending, difficult,
and sometimes dangerous fight against anthropocentrism.
Read about ancient mythologies on pages 5-15 of the textbook. Since we are
going to study modern, i.e. scientific cosmology, we
skip the mythology. Consider taking ASTR2000 Ancient Astronomies in the
fall!
SCIENTIFIC METHOD
The difference between the science and the myth is that a scientific
theory is based on observations and necessarily makes
predictions, which again can be tested by observing the
real universe.
The scientific description should be objective, i.e. any observation
or experiment should be reproducible by others.
GENERAL THEORY
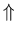
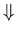
INDUCTION DEDUCTION
(from specific (from general
to general) to specific)
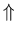
OBSERVATIONS PREDICTIONS
Specific instances Individual events
REQUIREMENTS TO THE SCIENTIFIC HYPOTHESIS
Hypothesis is an explanation of a particular phenomenon based on
the observational data.
Hypothesis must be:
- relevant (a pure thought does not work).
- falsifiable (this does not mean it is false).
- consistent with previously established theories;
- simple; this is sometimes called Occam razor
(for medieval English philosopher William of Occam).
- predictive (not the same as falsifiable).
 Example: a pen falls on the floor because
Example: a pen falls on the floor because
- A:
- the Earth gravity pulls it.
- B:
- all things want to move to the center of Earth.
- C:
- it just feels like doing that.
- D:
- it is the God's will.
LEVELS OF SCIENTIFIC TRUTH
- Theory: well established and well tested with the observations.
All relevant quantities are known to sufficient precision. Rarely,
if ever, wrong.
- Model: reasonably well established and tested with the
observations. Not all parameters are determined to high precision.
Rarely wrong.
- Hypothesis: plausible, but not well established; supported by
a limited set of observations. Sometimes wrong.
- Scenario: quite speculative, supported by only a few
observations, if any. Often wrong.
In this class we will be studying the Big Bang Theory, and how
it came into existence.
![]() Why does the universe seem to be made for
humans? Look, we get everything we need for our life from the nature around
us: water, food, fuel, materials for construction, etc.
Why does the universe seem to be made for
humans? Look, we get everything we need for our life from the nature around
us: water, food, fuel, materials for construction, etc.
![]() Example: a pen falls on the floor because
Example: a pen falls on the floor because