In this section I compare the effects of changing composition from the old Gustafsson mixture (X=70.2959%, Y=27.9161%), to the AG89 mixture and Z/X=0.0245 and Y=24.5%, by comparing the simulations sol50G and sol50.
There are two immediate effects of this change; The mean molecular weight,
![]() , decrease and the opacity increase because of the smaller content of the
opacity-wise inert helium.
, decrease and the opacity increase because of the smaller content of the
opacity-wise inert helium.
Hydrostatic equilibrium
results in an overall increase of the density by approximately the ![]() -ratio,
-ratio,
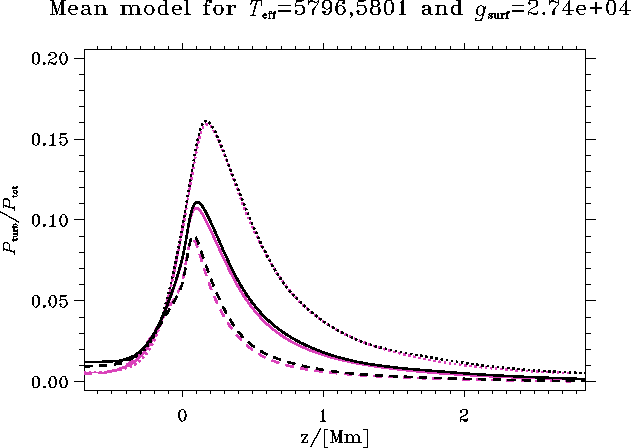
Figure 12: The turbulent- to total pressure ratio. Pink curves are for sol50
and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
as the main part of the pressure
![]()
is proportional to ![]() .
Dividing Eq. 2 with P we see that this causes a decrease
in the pressure scale height
.
Dividing Eq. 2 with P we see that this causes a decrease
in the pressure scale height
![]()
which disappears with depth though, due to a rise in temperature. The first
order effect is therefore a contraction of the atmosphere by the ratio of the
![]() 's for the two cases.
's for the two cases.
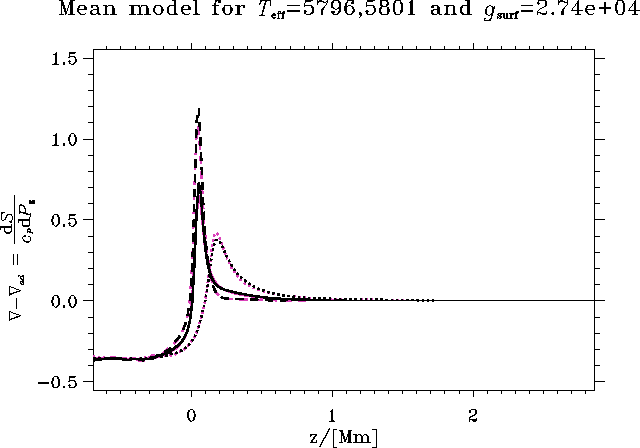
Figure 13: The superadiabatic gradient ![]() . Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
. Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
As the differences in composition also affects the
ionization structure, i.e. the ![]() ratio is not a constant but changes
with depth, other effects enters too.
ratio is not a constant but changes
with depth, other effects enters too.
From Fig. 13 and 14 we see that both the super adiabatic
gradient and the vertical velocities decrease, going from sol50G to sol50.
The total flux is maintained at ![]() K though, because of
the larger density. The
K though, because of
the larger density. The ![]() -peak in the downflow is increased
whereas the peak in the upflow and the total average is decreased
This is possible because the fillingfactor increases from
the
-peak in the downflow is increased
whereas the peak in the upflow and the total average is decreased
This is possible because the fillingfactor increases from
the ![]() -peak in the upflow and downwards, with about 3%,
effectively broadening the peak in the total average of
-peak in the upflow and downwards, with about 3%,
effectively broadening the peak in the total average of ![]() .
.
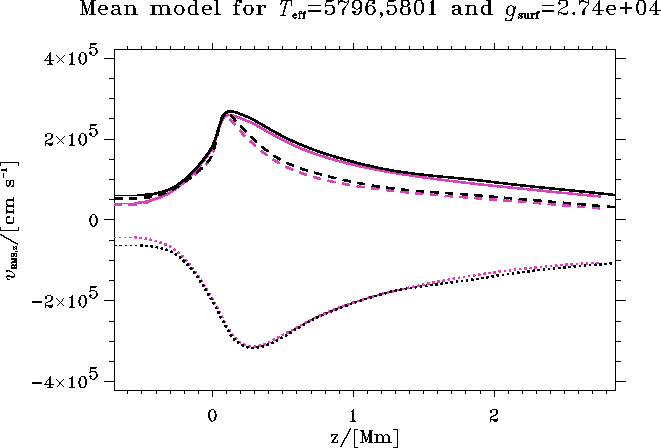
Figure 14: The vertical RMS velocity ![]() . Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
. Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
The horizontal velocities are in general smaller, but not by the same constant factor as is the case for the vertical velocities in the upflow, because of the changing fillingfactor.
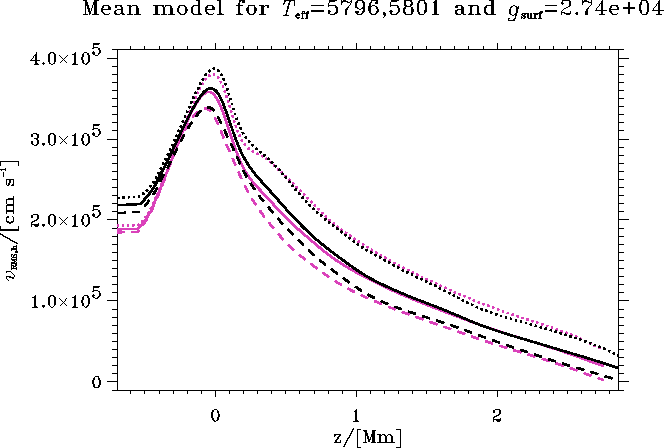
Figure 15: The horizontal RMS velocity ![]() . Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
. Pink curves are for
sol50 and black curves for sol50G.
I show both the total horizontal average (solid) as well as the
average in the upflow (dashed) and the downflow (dotted).
Last updated [an error occurred while processing this directive] by: trampedach@pa.msu.edu.